We are still actively working on the spam issue.
Anonymizing yourself
The internet is a cruel and horrible place. You might want to drop out of the matrix and join an anonymous network. A broad approach on how to start evading global data surveillance and improving your overall online privacy can be found here.
Anonymous Networks
Tor
Tor sets up a SOCKS proxy to the normal internet, allowing you to send any application’s connection anonymously through the Tor network. Any connections made through Tor will be anonymised but not confidential unless you use end to end encryption in the application, like SSL/TLS for web browsing, or an SSH tunnel. Torrenting is discouraged as it uses up too much bandwidth.
I2P
I2P is end to end encrypted and separate from the normal internet; this means that connections through I2P are confidential and anonymous. No-one can know who you are talking to, or what you are saying to them, because there are no exit nodes. Tor hidden services (.onions) work in a similar way. All internet applications can be forwarded through I2P including ed2k, Gnutella, and torrents. Torrenting is encouraged on the I2P network, although you cannot connect to non-I2P torrent swarms.
Freenet
Freenet is a distributed filesystem, where you can store files ‘in the cloud’ and download them anonymously from the Freenet network. Many of the files are HTML pages which can be viewed as static websites using a browser, and many are standalone files which can be searched and downloaded anonymously. Freenet content is undeletable as there is no way of knowing which node is holding each file.
Browsers
Safe Practices
- Always use an open-source browser. This ensures it can be freely audited. Remember: Google Chrome is not open-source, Chromium is.
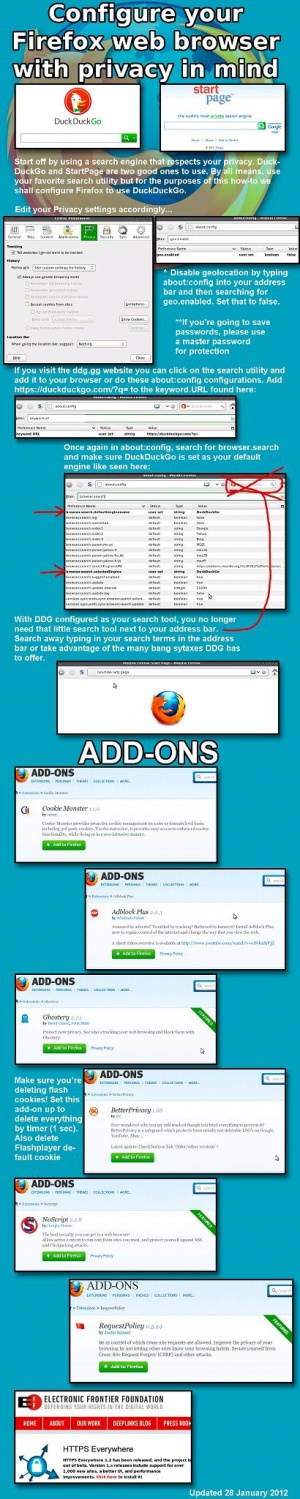
- Use a search engine that respects your privacy such as DuckDuckGo or StartPage instead of Google or Bing.
Mozilla Firefox
To ensure maximum security while browsing the internet, always turn off third party cookies. Mozilla describes them as: For example, cnn.com might have a Facebook like button on their site. That like button will set a cookie that can be read by Facebook. That would be considered a third-party cookie.
Change your search engine. There are ways to get around Google’s insane profiling. See: Guide To Search Engines.
Extensions
There are many extensions available for Firefox to make you less trackable.
- NoScript: Disables all JavaScript by default and explicitly asks you to confirm when it should be run. Not only does it help you become less trackable, but also more secure.
- Request Policy: Disables all cross-website requests (ex: images, javascript, flash) and forces you to make a whitelist of sites you trust. Also useful for blocking ads.
- Secret Agent: Continuously Randomizes your Firefox/SeaMonkey HTTP User Agent and other headers, to suppress device Fingerprinting, and resist web tracking. Note: Websites can still discover out your browser details by other means. (see: Fingerprinting methods)
Read the Firefox article for a more comprehensive list of addons.
Fingerprinting Methods
- Plugins such as Flash or Java.
- Client-Side Scripting (JavaScript).
- HTTP Header information (such as testing to see how/which response headers are obeyed, and how response codes are interpreted by the client).
- See also: EFF Panopticlick
DNS
DNS is what allows your computer to convert a domain name (such as wiki.installgentoo.com) into an IP address to connect to. That process is called resolving. When your computer attempts to resolve a domain name it queries a DNS server. Usually this will belong to your ISP if you have not configured it manually. Not all DNS servers are created equal. Some block queries to certain websites, some hijack queries and redirect them elsewhere, and some log your queries. You should look for a DNS server that is close by (to reduce latency in your requests) that doesn't log your IP address. In addition, you may want to use DNSCrypt for added protection.
Warning: Google DNS and OpenDNS log queries. Google "anonymizes" query information after a period of time, but keeps associated ISP information permanently.[1] OpenDNS logs your IP address and may also correlate it with other information that is normally non-personally identifying.[2] Avoid those two services.
DNSCrypt
See DNSCrypt
Operating Systems
While unfortunately, government organizations around the world have a variety of backdoors into a variety of operating systems, one can still attempt to be anonymous through a variety of methods. Free software alternatives to Windows or Mac OS appear to be more secure than their counterparts, since their code is almost always individually reviewed.
Tails
Tails is an OS specifically created to aim at preserving your privacy and anonymity. It forward all your packets through TOR network and leave no trace on the computer you are using it on. Your files and emails are also encrypted using top of the line cryptographic tools.
Android
By their nature cellphones cannot be completely anonymous, but there are some steps that can be taken to at least limit your footprint.
Android Replacements
- Replicant: A project to completely replace all proprietary components of Android.
- Custom ROMs
- Firefox OS: An alternative operating system by Mozilla that runs on some Android devices.
Alternative Google Apps
- F-Droid: Part of the Replicant project. An app store that only contains Free Open Source Software.
- NOGAPPS Project: Replaces the Play Store, Google Maps API, Network Location API, and others in the future.
- APK Downloader
- OsmAnd~: Replacement for Google Maps.
- GApps Browser
Removing Ads
- AdAway: Hosts file based ad-blocking. (Requires root)
- Adblock Plus
- Lucky Patcher: Patches APKs to remove ads and allows you to disable the ad's activity itself. (Requires root)
Enforcing Permissions
- XPrivacy
- App Ops: Available since Android 4.3. Removed in 4.4.2, but still retained in custom ROMs. Allows you to tweak individual permissions on a per-app basis.