We are still actively working on the spam issue.
Difference between revisions of "Compact Disc"
m (fixed interwiki links) |
m (Change "Compact Tape" to Compact Cassette", add link to page) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
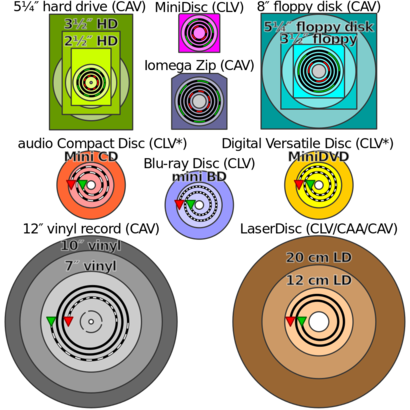
| − | + | [[File:Comparison disk storage.svg.png|thumb|upright=1.35|Comparison of several forms of disk storage showing tracks (not-to-scale); green denotes start and red denotes end.<br /><nowiki>*</nowiki> Some CD-R(W) and DVD-R(W)/DVD+R(W) recorders operate in ZCLV, CAA or CAV modes.]] | |
A '''Compact Disc''' (or CD) is a common form of multimedia [[Storage devices | storage]] that was created in the 1970's, but was not widely used until the mid to late 1990's. It has been largely replaced by computer digitization. | A '''Compact Disc''' (or CD) is a common form of multimedia [[Storage devices | storage]] that was created in the 1970's, but was not widely used until the mid to late 1990's. It has been largely replaced by computer digitization. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The reason for the name is due to Panasonic, where it was originally invented. Panasonic already had the [[Compact Cassette]] (known commonly as Audio Tape, not to be confused as 8-Track Tape), and decided to name their optical storage system after it. | ||
| + | |||
| + | CDs have standard sizes, one supporting 600MB and the other supporting 700MB. Many variations of CDs have been created over the years, notably Phillips CDi (for video games), Enhanced CD, and CD Video. These formats have since fallen out of fashion. | ||
== Audio CDs == | == Audio CDs == | ||
| − | Many legacy [[:Category:Hardware | hardware]] devices (such as car stereos) still | + | Many legacy [[:Category:Hardware | hardware]] devices (such as car stereos) still support Audio CDs. |
| + | |||
A common problem with user-written discs is that the wrong burn type is selected when creating the cd, causing the legacy hardware to reject the disc. | A common problem with user-written discs is that the wrong burn type is selected when creating the cd, causing the legacy hardware to reject the disc. | ||
| − | '''DAO''' ('''Disc at Once''') is the correct burn setting when creating an audio cd. This "closes" the disc to any further writing and causes the disc to behave as any commercially bought audio | + | |
| + | '''DAO''' ('''Disc at Once''') is the correct burn setting when creating an audio cd. This "closes" the disc to any further writing and causes the disc to behave as any commercially bought audio CD. | ||
| + | |||
The opposite of DAO is '''SAO''' ('''Session at Once''') which allows further writing to the disc in any unused space, but is generally incompatible with CD Audio players. | The opposite of DAO is '''SAO''' ('''Session at Once''') which allows further writing to the disc in any unused space, but is generally incompatible with CD Audio players. | ||
: Some audio cd hardware was designed as "burnt cd friendly", meaning that it understood unclosed discs. These are fairly uncommon. | : Some audio cd hardware was designed as "burnt cd friendly", meaning that it understood unclosed discs. These are fairly uncommon. | ||
| + | |||
| + | All players support the raw audio format WAV. Most contemporary players support MP3 format. Sadly, these are the only two formats that players support. Perhaps someday they will make players capable of playing FLAC or OGG, but it doesn't look hopeful. | ||
== External Links == | == External Links == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 24: | ||
[[Category:Terms]] | [[Category:Terms]] | ||
[[Category:Hardware]] | [[Category:Hardware]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Audio]] | ||
Latest revision as of 02:36, 22 April 2019
A Compact Disc (or CD) is a common form of multimedia storage that was created in the 1970's, but was not widely used until the mid to late 1990's. It has been largely replaced by computer digitization.
The reason for the name is due to Panasonic, where it was originally invented. Panasonic already had the Compact Cassette (known commonly as Audio Tape, not to be confused as 8-Track Tape), and decided to name their optical storage system after it.
CDs have standard sizes, one supporting 600MB and the other supporting 700MB. Many variations of CDs have been created over the years, notably Phillips CDi (for video games), Enhanced CD, and CD Video. These formats have since fallen out of fashion.
Audio CDs
Many legacy hardware devices (such as car stereos) still support Audio CDs.
A common problem with user-written discs is that the wrong burn type is selected when creating the cd, causing the legacy hardware to reject the disc.
DAO (Disc at Once) is the correct burn setting when creating an audio cd. This "closes" the disc to any further writing and causes the disc to behave as any commercially bought audio CD.
The opposite of DAO is SAO (Session at Once) which allows further writing to the disc in any unused space, but is generally incompatible with CD Audio players.
- Some audio cd hardware was designed as "burnt cd friendly", meaning that it understood unclosed discs. These are fairly uncommon.
All players support the raw audio format WAV. Most contemporary players support MP3 format. Sadly, these are the only two formats that players support. Perhaps someday they will make players capable of playing FLAC or OGG, but it doesn't look hopeful.