We are still actively working on the spam issue.
Home server/Routing for retards
Networking guide and recommendations for homelabs.
Contents
General scope and purpose of this guide
The point is to get (you) into networking, provide some best practises and software/learning suggestions, and show some ez mode copy and paste commands to set up some enterprise tier routing on commodity hardware.
Where to learn networking
Books
- Data Communications and Networking ISBN: 978-0073376226
Router hardware
DIY
Generally speaking, any CPU made in the last 10 years is capable of forwarding gigabit network traffic so the requirements for DIY routing is pretty damn low. The same is true for memory and disk, just the bare minimum will do.
Some things to consider are if you need multiple NICs (or is it more economical to pick up a managed switch and run a router on a stick configuration), do you want to do HA with multiple boxes, and it's good to stick to brand name peripherals as you're guaranteed compatibility and hardware offload features.
Appliance
There are a lot of options out there, most of them are pretty awful. The best bet for learning is getting your hands on some old Cisco gear, however the ones that seem affordable are usually quite limited both in software options and hardware capability (usually only one or two gigabit ports, abysmal throughput and shit loads of sploits because it's last firmware release was in 2008).
Avoid Juniper for the above reasons and because they now use a subscription model so you might be able to buy a very nearly new box for next to nothing but you won't be able to update it or it just won't have any OS at all unless you can pull $5k out of your ass.
Recommended brands if you really can't be fucked rolling your own:
Prosumer
- Ubiquity
- EnGenius
- MikroTik
Enterprise
- Cisco
- Aruba
- Dell
- HP
Routing software
VyOS
Text mode Linux router with JunOS inspired interface. A long distant fork of Vyatta Core it also has many modern features such as Wireguard VPN, PBR, zone based firewalls, FRR (BGP/OSPFv3/BFD), EVPN+VXLAN and VRRP.
Text mode only, commit and save are explicit with boot/runtime configuration as well as diff-able history and rollback from bootloader.
Pros
- Boots in literal seconds
- Very cool TUI, the entire system is one big conf file
- There are
Cons
- Steep learning curve
- If you forget to save everything you did is lost on reboot
- WAN load balancer is full of bugs, avoid
Further reading:
pfsense
Great all rounder that's based on FreeBSD, has many modern and advanced features such as Wireguard VPN, PBR and does some fancy L7 DPI/filtering.
This is a GUI managed system with implied commit and save work flow.
Pros
- Good for beginners through professional users
- Lots of features (like all of them)
- Easy to use GUI
Cons
- Bloat
- Save on commit with no discard/rollback mechanism
- Many options with no real clues as to which ones are required or optional
Further reading:
Switch hardware
For a home lab you really only need a L2 managed switch, "L3" features like voice vlans or static routing is going to be pointless or slow as shit on old used hardware, the L2 stuff is always line speed and just about everything made in the last 15 years is going to do the job.
Prosumer
- Ubiquity
- Edimax
- MikroTik
Enterprise
- Cisco
- Aruba
- Dell
- HP
Basics: Private subnet to keep mom from finding my furry porn
The idea here is we want to run a separate network from the default LAN provided by the ISP router. Housemates use the "LAN" as usual but we put all of /hsg/ boxes behind a another router. This keeps your gear safe from prying eyes and also protects normies if you get your shit hacked.
Basics: Firewalls
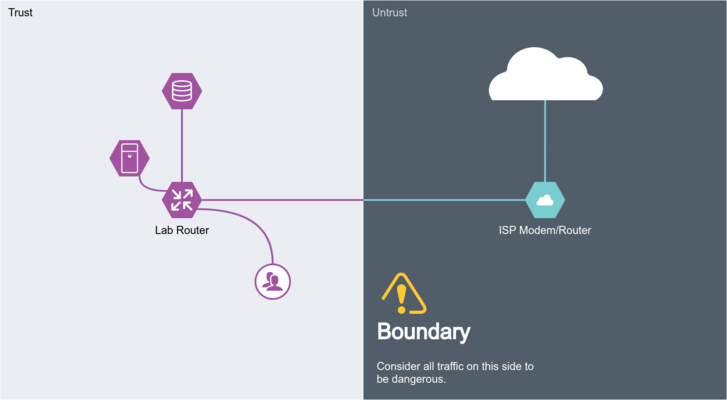
Firewalls are pretty straight forward, all we want to do is keep the weirdo's out while not locking ourself out of the router. As a general rule we split our network into two zones, trust and untrust.
Trust is our LAN, for simplicity sake even if we are running multiple subnets there isn't much point firewalling traffic between them so they all belong here. And we want to be able to send arbitrary traffic to the untrust zone, since there's no way to list ALL of the sites or servers out on the internet that you might care to visit.
Untrust is the internet and any subnets connected to the internet in an unprotected way (i.e. port forwarding). This zone should not be able to pass traffic to our trust zone unless it was originated by the trust zone... originally.
Basics: Port forwarding over CGNAT
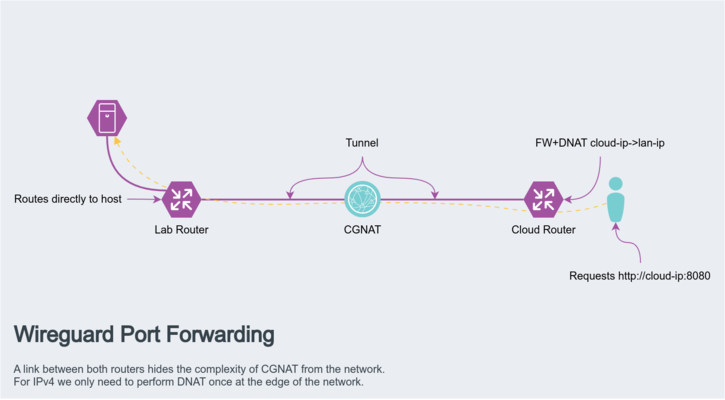
Let's say you have some service or vidya game you wish to share publicly, you have the hardware to do it, the internet connection to handle the bandwidth, but you can't actually accept the incoming traffic as you don't have a public IP or your IP changes so often even DDNS can't keep up.
One way around this is using a VPN, but rather than going site to site (since neither you or your client have a routable public address) we can do site to hub. A cloud server is used as the hub, this has the advantage that it's already on a very fast network with a static IP and no restrictions on what traffic you can receive. It can also be quite cost effective as you can use hourly billed cloud providers if you only need the functionality on rare occasions. For what constitutes a "router" is up to you, but installing actual router platforms like pfsense is recommended since they are designed for the task and often provide much easier ways to configure this shit than "just run a script lmao".
In order for this to work you need both routers to know about both networks, your LAN and the cloud servers.
Local routing table:
S>* 0.0.0.0/0 [0/0] via 192.168.101.1, eth1, weight 1, 23:14:50 S>* 172.105.182.0/24 [200/0] via 10.251.1.1, wg1, weight 1, 00:16:44 C>* 192.168.0.0/24 is directly connected, eth0, 4d18h07m C>* 192.168.101.0/24 is directly connected, eth1, 4d18h07m C>* 10.251.1.0/30 is directly connected, wg1, 4d18h07m
Remote routing table:
S>* 0.0.0.0/0 [0/0] via 172.105.182.1, eth0, weight 1, 23:14:50 S>* 192.168.0.0/24 [200/0] via 10.251.1.2, wg1, weight 1, 00:16:44 C>* 172.105.182.0/24 is directly connected, eth0, 4d18h07m C>* 10.251.1.0/30 is directly connected, wg1, 4d18h07m
In this example the tunnel itself uses are transit network of 10.251.1.0/30, which means you have an IP for the two routers and nothing else, make sure you add them to the allowed-ips parameter in the peer section, as well as the networks you wish to route.